By Nitin Thapar - https://blog.quantinsti.com/evolution-trading-barter-system-algo-trading/
The History of Trade
The evolution of trading is one of the most significant factors in the journey of mankind. Humans have evolved throughout the centuries and that would not have been possible if they were restricted to geographical boundaries.
Trading is a system of bringing people together for mutual benefit, though the primitive societies saw gatherings of people only in religious and cultural events which were limited by custom or kinship.
Today, trade has led to both static and dynamic gains for countries. Trade has inspired innovation of techniques which has led to faster and better communication between nations, creating a unified world for trading. Let me take you through the ‘Journey of Trade’ which has played a crucial part in shaping the modern day economy and learn how simple exchange of goods and services matured into a much more complex stock trading practices.
The Origins of Trade
Trade Before Civilization: Trading Stones

The Stone Age began roughly 2.6 million years ago; during this era the stone tools were used for hunting and people were self-sufficient. They traveled in search of food and shelter, trade was conducted in relatively smaller scale, within small communities, and over a shorter distance. There was no concept of farming and merchants in the early Stone Age (Palaeolithic stage of the Stone Age). Trading was the main facility of prehistoric people, who bartered goods and services including hunting equipment and stones considered to have great value.
Currency Used: Barter system
17,000 BC to 9000 BC
The First Long-Distance Trade: Obsidian & Agriculture
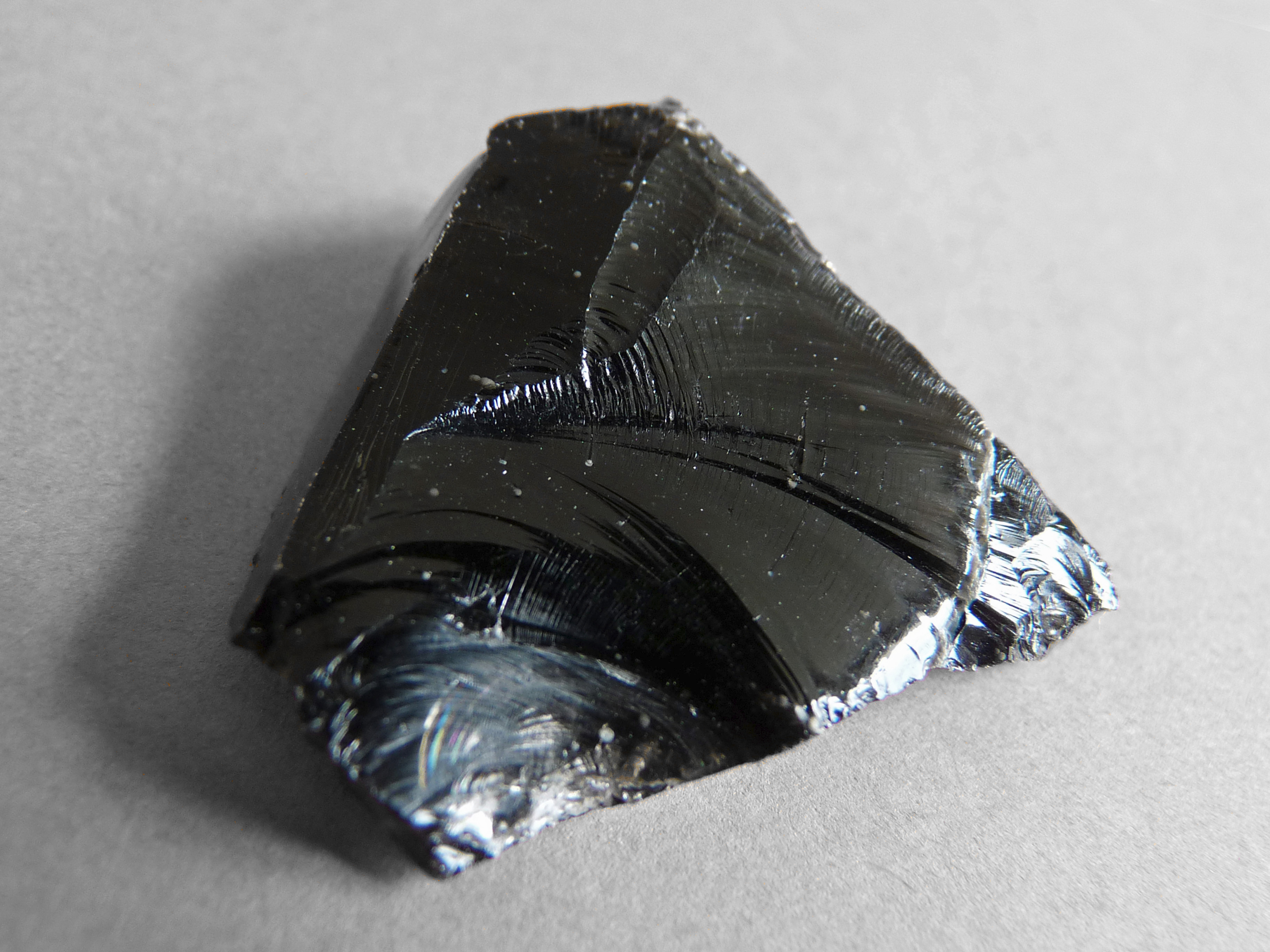

Obsidian

Harvest is shown a wall painting in the Tomb of Menena
Obsidian was a widely used trade item post 17,000 BC because of the great desirability of this material before the use of metals. Obsidian was used to make cutting tools and was preferred over other available materials since it also signified the higher status of the tribe.
Obsidian was traded at distances of 900 kilometers within the Mediterranean region.
With the introduction of the new Stone Age era (Neolithic Phase) i.e starting 9000 BC agriculture started developing, people started domesticating animals and growing crops which led to communities settling in one location.
With agriculture and new farming tools, there was more surplus of food which was used for trading in exchange for other useful commodities (Barter System). Trading started between different communities where not only surplus of food but also farming tools (tools made from stone) and crafts were exchanged. With this, a new social class of merchants came into existence; they would travel thousands of miles on foot to conduct trade with other communities.
Currency Used: Commodities in the form of livestock, salt, metal, rare stones etc
8,000 BC to 6000 BC
Matured Trading System: Civilization on the Rise
It’s 8000 BC and the world population is around 5,000,000. People have now learned the art of farming, domesticating animals, agriculture is booming and a food-producing economy has emerged.
Pottery traditions were on the rise in parts of the world now known as Asia, Japan, Korea, China, Mexico and many more. Obsidian was still an important part of trading habit but there was more to trade (barter) now including livestock, surplus production, salt, copper, cowry shells, pottery, animal skins, farming tools, seeds etc.

Korean neolithic pot, found in Busan
In the next few centuries’ people started inhabiting other parts of the world including Indus Valley, Jordan, Ireland, Anatolia, Scotland, North America, Nigeria, Turkey, Norway, Italy, Europe, Egypt etc. Ornaments (Gold & Copper) came into existence and were in huge demand around the world.
Based on the inhabitant region these cultural group of people started accommodating necessities based on the availability of natural resources in the adjacent areas. Objects were now made with an aesthetic value and not just limited to function.
Newly settled people now started importing exotic goods over distances of many hundreds of miles.
Currency Used: Money in the form of objects such as weapons, metal artifacts, pottery, copper, plant produce.
5,000 BC to 4000 BC
Important Inventions: The fast & Chronicle
The invention and development of ‘Wheel’ is an important part of the trading history. This civilization that witnessed the use of wheel had a better advantage over their ancestors because they had a greater ability to produce food, manufacture goods, and transport people and goods at a greater distance.

The earliest wheels were made of a solid piece of wood.
Communities started expanding since it became easier for them to cover greater distance within a short period of time and there was no need to stay close to food production areas. The wheel was also used in making pottery; it was an important part of early civilization.
The period from 5th Millennium to 4th Millennium is also important because this is when proto-writing or the first form of writing was discovered. People were now able to commute and communicate better.

Clay amulet, one of the Tărtăria tablets, dated to ca. 4500 BCE
Currency Used: Barter, clay pots or tools, seeds, grains, tools etc
3,000 BC to 1000 BC
International trade on the rise: The caravans of India
Ebla (Syria) became a prominent trading center in the third millennium. Trade flourished between communities that were part of different kingdoms. With more inventions acting as a catalyst for trade related activities the flow of goods increased and the new set of occupations were acquired.
By the second millennium BC, former backwater island Cyprus had become a major Mediterranean player by ferrying its vast copper resources to the Near East and Egypt, regions wealthy due to their own natural resources such as papyrus and wool. Phoenicia, famous for its seafaring expertise, hawked it's valuable cedar wood and linens dyes all over the Mediterranean. China prospered by trading jade, spices and later, silk. Britain shared its abundance of tin.
With the domestication of camels, trade routes over land became popular and the group of traders called caravans used these trade routes to carry trades with India and Mediterranean. Towns began sprouting up like never before with pit-stop or caravan-to-ship port emerging everywhere.

A Caravan of camels travels through a starlit desert night
Source: sahapedia.org
It was during this time that the Incense Route was used to transport frankincense and myrrh which was used as oil, perfume, incense, and medicine, which was only found in the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula (modern Yemen and Oman).
Currency Used: Gold, silver, bronze, cattle, cowry shells, salt, commodity exchange etc
700 BC to 1500 AD
Trading Routes: Year of the Lord and Much More

The city of Vulci became the hub of trading and manufacturing center.
Greek colonists set up trade centers at Salona. The establishment of colonies permitted the import and export of luxury goods such as pottery, wine, oil, metalwork, and textiles.
The Han Dynasty opened up the 'Silk Road' trading route between China and Central Asia. Many different kinds of merchandise traveled along the Silk Road, it is one of the oldest routes of international trade in the world.
The first non-stop voyages from Egypt to India were initiated at the start of the Common Era. Spices from India became famous around the world and were the main exports to the western world. The spice trade fostered new diplomatic relationships between East and West, it was partly the spice trade in mind that Christopher set out in 1492 and ended up finding America)
With the start of 7th century AD the ‘Tea Horse Road’ was used to trade Chinese tea and Tibetan warhorses. This route was spread over 6000 miles and was majorly used to export tea from China to Tibet and India.
Trading of gold, salt and cloth were also booming in Africa thanks to the Trans-Saharan Trade Route from North Africa to West Africa. These trade routes first emerged in the 4th century AD and by the 11th century AD caravans of over a thousand camels would carry goods across the Sahara desert.
Currency Used: Starting from metal in the shape of small knives and spades made of bronze to first manufactured coins in India and China, minted coins to bills of exchange.
The Evolution of Stock Exchange
1531: Belgium boasted a stock exchange in Antwerp. Brokers and money lenders would meet there to deal in business, government and even individual debt issues. There were no promissory notes and bonds or real stocks.

1600s: East India companies formed which changed the way business was done. The stock of these companies would pay dividends on all the proceeds from all the voyages the companies undertook. These were the first modern joint stock companies. This allowed the companies to demand more for their shares and build larger fleets. The profit for investors was based on the size of the companies, combined with royal charters forbidding competition.

East India House in Leadenhall Street, London
1773: The first stock exchange in London was officially formed
1780s: Japanese trader invents candlestick patterns to predict price movements in the rice market. 1790: The birth of U.S. investment markets was marked with the federal government issuing $80 million in bonds to repay Revolutionary War debt. Two years later the “Buttonwood Agreement” was signed by 24 stockbrokers and later moved to the Tontine Coffee House for trade.
1792: NYSE acquires first traded securities
1817: The constitution of NYSE is adopted
1830s: For the first time trading on corporate stocks and shares in Bank and cotton presses took place in Bombay.
1840s: During the California Gold Rush, curbstone brokers generated market opportunities for mining companies, facilitating the development of a new and rapidly growing industry.
1856: An informal group of 22 stockbrokers with a then princely amount of Rupee 1 started investing under a banyan tree opposite the Town Hall of Bombay from the mid-1850s. The same banyan tree still stands in the Horniman Circle Park in Mumbai.
1859: Oil stocks traded on the curb market after the discovery of Petroleum in western Pennsylvania.
1860: The exchange flourished with 60 brokers. In fact, the 'Share Mania' in India began when the American Civil War broke and the cotton supply from the US to Europe stopped. Further, the brokers increased to 250. An informal group of stockbrokers organized themselves as the “The Native Share and Stockbrokers Association” which in 1875, was formally organized as the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).

Present Day Bombay Stock Exchange building in Mumbai, India
1864: Founded in part by former curbstone brokers, Open Board of Stock Brokers started functioning. It got merged with the New York Stock Exchange in 1869.
1875: BSE, on the other hand, was set up in the year 1875 and is the oldest stock exchange in Asia. It has evolved into its present status as the premier stock exchange.
1890s: The curb market moves to Broad Street near Exchange Place.
1904: Emanuel S. Mendels started to organize the curb market to encourage sound and ethical dealings. The New York Curb Market Agency was established in 1908 to codify trading practices.
1921: The New York Curb Market found a new home indoors to a new building on Greenwich Street, Lower Manhattan.
1944: The New York Curb Market was formed with a constitution that sets higher brokerage and listing standards.
1956: The Government of India recognized the Bombay Stock Exchange as the first stock exchange in the country under the Securities Contracts (Regulation) Act.
1960: The online stock trading accounts did not exist in the 1960s. The order booking process was initiated by calling your broker and asking him to enter the order in his own system, on your behalf. In case the stock that was ordered is traded in the NYSE, it was called onto the floor of the NYSE e.g. order to buy 100 shares was matched with an order to sell 100 shares in the broker’s system.
If it was an over-the-counter (OTC) stock, that is, one not listed on the NYSE or AmEx but still traded, the broker called around by phone to market makers who quoted different prices to buy or sell the stock.
1969: In order to allow brokers to post offers to buy and sell stocks after regular market hours, Instinet is founded as the first Electronic Communication Network (ECN)
1970s: Founding of NASDAQ.
1971: The National Association of Securities Dealers, an association of over-the counter (OTC) market makers formed in 1939, created the first electronic stock market: the National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (NASDAQ) market.
1975: Fixed commissions are abolished by the SEC. This allowed for the rise of discounted commissions and facilitated the growth of Charles Schwab and others. The Amex launches its options market.
1976: NYSE introduces its Designated Order Turnaround (DOT) system, which allowed brokers to route 100-share order directly to specialists on the floor. These were not true electronic executions since the specialist still matched the orders, but it did bypass floor brokers.
1980s: The rise of electronic trading.
1984: NYSE adopts a more sophisticated SuperDOT system that allows orders up to 100,000 shares to be routed directly to the floor. More floor brokers cut out.
1987: The 1987 crash is blamed partly on "portfolio insurance" (shorting stock index futures against a stock portfolio). Electronic trading takes another leap forward as NASDAQ expands the Small Order Execution System (SOES), which allows dealers with small trades to enter their orders electronically rather than over the phone. This was done because during the 1987 crash many broker-dealers simply stopped answering their phones.

Stock Brokers in the 1980s
1990-95: the rise of online trading.
1994: NSE started trading on 4 November 1994. Within less than a year, NSE turnover exceeded the BSE.
1996-1999: Online trading begins to explode as Internet traffic dramatically increases. Small traders suddenly had the same access to real-time pricing as professional brokers. The word "day trader" enters the vocabulary.
The 2000s: Decimalization, algorithmic trading, and high-frequency trading.
2000: The NASD spins off NASDAQ into a publicly traded company.
2001: Stock trading in pennies begins. NYSE introduced Direct+, which facilitated immediate automatic execution of limit orders up to 1099 shares. This is real electronic trading (automated matching of buy and sell orders) and was the beginning of the end of the old floor specialist system.
2005: Reg-NMS changes everything- HFT goes prime time. The SEC consolidates all rules on the national market system into Reg-NMS, which forced the NYSE to go electronic and fostered the growth of competing ECNs and exchanges.
NYSE launches NYSE Hybrid in December, which attempts to combine the NYSE floor operations with electronic trading occurring off the floor. The 1,099 share limits on the Direct+ system were removed. Specialist participation in the marketplace started to drop drastically.
2006: NYSE demutualizes, becomes a for-profit and publicly traded company. This gives the exchanges an incentive to start managing for profit and more incentive based competition for brokers.
2007: NYSE merges with Euronext, which had been formed in 2000 through the merger of the Amsterdam, Brussels, and Paris exchanges.
2008: NYSE eliminates specialists, renaming them Designated Market Makers, though still in charge of maintaining a fair and orderly market in their stocks. Algo trading begins in India.

Algorithmic Trading - Percentage of Market Volume
2009: Credit Suisse’s Advanced Execution Services (AES) unit launched algorithmic trading in Indian equities. The AES suite of algorithms included traditional algorithmic strategies that seek to divide trading volumes up over time and strategies that seek to trade at the Volume Weighted Average Price of a stock.
The Same year, a software developer Satoshi Nakamoto proposed bitcoin, which was an electronic payment system based on mathematical proof.
2010: Direct Edge, formerly an ECN, becomes an exchange. In India, National Stock Exchange (NSE) started offering additional 54 co-location server ‘racks’ on lease to broking firms from June 2010 in an effort to improve the speed in trading. Also, adapts FIX protocol. Multiple QuantInsti, Asia’s pioneer in Algo trading education is launched and started first algo trading education programme in India.
2012: NYSE created something called a single-stock circuit breaker. If the Dow drops by a specific number of points in a specific period of time, then the circuit breaker will automatically halt trading. This system is designed to reduce the likelihood of a stock market crash and, when a crash occurs, limit the damage of a crash.
At the close of 2012, the size of the world stock market (total market capitalisation) was about US$55 trillion. By country, the largest market was the United States (about 34%), followed by Japan (about 6%) and the United Kingdom (about 6%)
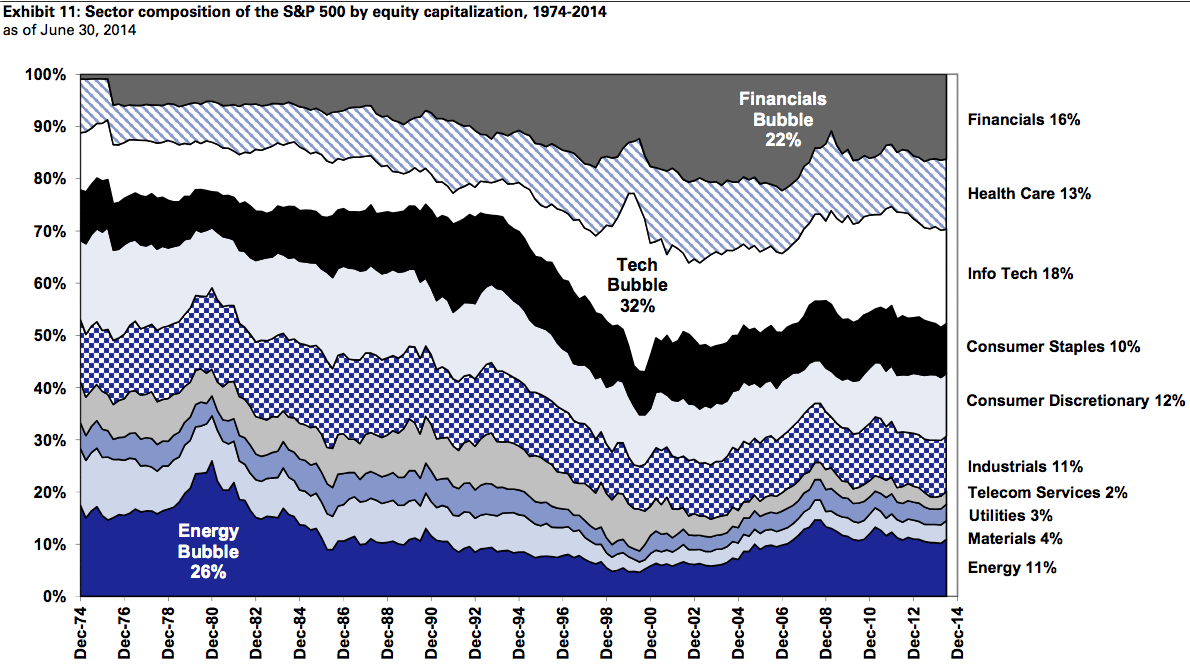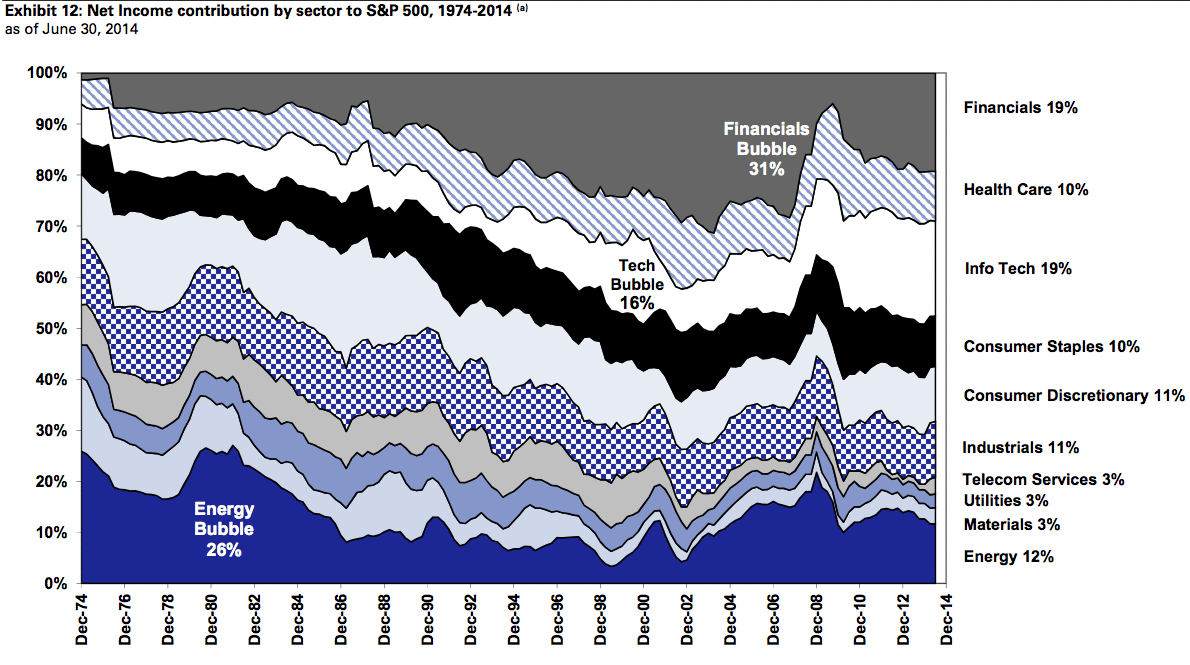
The 40-year evolution of the American stock market in a single GIF
Source: https://qz.com/230196/the-40-year-evolution-of-the-american-stockmarket-in-a-single-gif/
2013: About 70% of US equities in 2013 were accounted for by Automated Trading. Algorithmic trading accounted for a third of the total volume on Indian cash shares and almost half of the volume in the derivatives segment.
2015: Social media integration; Bloomberg Terminals incorporates live Tweets into its economic data service. Bloomberg Social Velocity tracks abnormal spiked in chatter about specific companies.
2017: Nasdaq smashes 6,000 and world stocks hit new high.
Nasdaq ended up 41.7 points at 6,025.5, having earlier hit a new lifetime high of 6,031.91. The milestone comes more than 17 years after the index touched the 5,000 mark.
As rightly quoted by Isabel Hoving “The positive aspect of the trade is that the world gets stirred up together”, for centuries we human beings have thrived by helping each other which has brought the world together. The evolution of trading was just a part of this journey but we are yet to witness what innovative approaches are to be followed in the near future which will shape the economy for the generations to come.
The Evolution of Trading from Barter System to Algo Trading
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/evolution-trading-barter-system-algo-nitin-thapar