In the first example below people whitness a stabbing but do not help because other people are watching and this diffuses the responsibility, but in the second example people are confined in a moving subway and help the victim no matter what.
[1] The Uninvolved Bystander as Conformist
In 1964, a young woman named Kitty Genovese was stabbed to death in New York City. This was a tragic event but not, in itself, a particularly novel occurrence. After all, in a major population center, brutal murders are not uncommon. What is interesting about this event is that no fewer than 38 of her neighbors came to their windows at 3:00 A.M. in response to her screams of terror and remained at their windows watching in fascination for the 30 minutes it took her assailant to complete his grisly deed, during which time he returned for three separate attacks. No one came to her assistance; no one so much as lifted the phone to call the police until it was too late. Why?
Well, perhaps the onlookers were sleepy or dazed. After all, people are hardly in full control of their mental faculties at three o'clock in the morning. Perhaps. But it was in broad daylight that Eleanor Bradley, while shopping on Fifth Avenue in New York City, tripped, fell, and broke her leg. She lay there for 40 minutes in a state of shock while literally hundreds of passersby paused momentarily to gawk at her and then kept on walking.
Why did these bystanders fail to help? Are people impervious to the distress of others? Have they become so accustomed to disaster that they can be nonchalant in the face of pain and violence? Were the bystanders in these situations different from you and me in some way? The answer to all of these questions appears to be no. Interviews conducted with the bystanders in the Genovese murder revealed that they were anything but nonchalant—they were horrified. Why, then, didn't they intervene? This is a difficult question to answer.
...the large number of people witnessing the tragedies militated against anyone's helping—that is, a victim is less likely to get help if a large number of people are watching his or her distress. Thus, nonintervention can be viewed as an act of conformity. In this case it appears that, for each individual, the other people were defining the reasonableness and appropriateness of helping or not helping. As we have seen, it is often reasonable to take one's cue from others.
[2] Dilemma - Bystander in an Enclosed Space
An experiment performed by Irving Piliavin and his associates in one of the cars of a train in the New York City subway system. In this experiment, an accomplice of the experimenters staggered and collapsed in the presence of several individuals riding the subway. The "victim" remained stretched out on the floor of the train, staring at the ceiling. This scene was repeated 103 times under a variety of conditions. The most striking result was that, a large part of the time, people spontaneously rushed to the aid of the "stricken" individual. This was especially true when the victim was made to seem obviously ill; in more than 95 percent of the trials, someone offered help immediately. Even when the "victim" had been given a liquor bottle to carry and was made to reek of alcohol, he received immediate help from someone on 50 percent of the trials. Unlike the behavior of the subjects that Darley and Latane dealt with, the helping behavior of the people on the subway train was not affected by the number of bystanders. People helped just as often and just as speedily on crowded trains (where there could be a diffusion of responsibility) as they did on virtually empty trains.
(1) people riding on the same subway car do have the feeling of sharing a common fate, and
(2) they were in a face-to-face situation with the victim from which there was no immediate escape.
How can the tendency to help be increased? Consider the questions that would run through your mind should you confront a possible emergency: Is the situation really serious? Does it require my personal intervention? Will helping be difficult or costly for me? Will my help benefit the victim? Can I easily leave? Your response will depend on your answers to each of these questions.
The Social Animal - Elliot Aronson - 8th Edition 1999
http://www.amazon.com/exec/obidos/ASIN/0716733129/
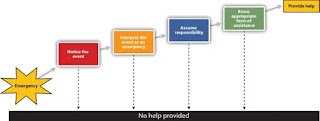
Decision Model of Helping
Latané & Darley (1970) formulated a five-stage model to explain why bystanders at emergencies sometimes do and sometimes do not offer help.
At each stage in the model the answer ‘No’ results in no help being given, while the answer ‘yes’ leads the individual closer to offering help.
However, they argued that helping responses may be inhibited at any stage of the process. For example, the bystander may not notice the situation or the situation may be ambiguous and not readily interpretable as an emergency.
The five stages are:
- The bystander must notice that something is amiss.
- The bystander must define that situation as an emergency.
- The bystander must assess how personally responsible they feel.
- The bystander must decide how best to offer assistance.
- The bystander must act on that decision.
Figure 1. Decision Model of Helping by Latané and Darley (1970).
Why does the bystander effect occur?
Latane and Darley (1970) identified three different psychological processes that might interfere with the completion of this sequence.
1. Diffusion of Responsibility
The first process is diffusion of responsibility, which refers to the tendency to subjectively divide the personal responsibility to help by the number of bystanders.
Diffusion of responsibility occurs when a duty or task is shared between a group of people instead of only one person.
Whenever there is an emergency situation in which more than one person is present, there is a diffusion of responsibility. There are three ideas that categorize this phenomenon:
- The moral obligation to help does not fall only on one person, but the whole group that is witnessing the emergency.
- The blame for not helping can be shared instead of resting on only one person.
- The belief that another bystander in the group will offer help.
Darley and Latané (1968) tested this hypothesis by engineering an emergency situation and measuring how long it took for participants to get help.
College students were ushered into a solitary room under the impression that a conversation centered around learning in a “high stress, high urban environment” would ensue.
This discussion occurred with “other participants” that were in their own room as well (the other participants were just records playing). Each participant would speak one at a time into a microphone.
After a round of discussion, one of the participants would have a “seizure” in the middle of the discussion; the amount of time that it took the college student to obtain help from the research assistant that was outside of the room was measured. If the student did not get help after six minutes, the experiment was cut off.
Darley and Latané (1968) believed that the more “people” there were in the discussion, the longer it would take subjects to get help.
The results were in line with that hypothesis. The smaller the group, the more likely the “victim” was to receive timely help.
Still, those who did not get help showed signs of nervousness and concern for the victim. The researchers believed that the signs of nervousness highlight that the college student participants were most likely still deciding the best course of action; this contrasts with the leaders of the time who believed inaction was due to indifference.
This experiment showcased the effect of diffusion of responsibility on the bystander effect.
2. Evaluation Apprehension
The second process is evaluation apprehension, which refers to the fear of being judged by others when acting publicly.
People may also experience evaluation apprehension and fear losing face in front of the other bystanders.
Individuals may feel afraid of being superseded by a superior helper, offering unwanted assistance, or facing the legal consequences of offering inferior and possibly dangerous assistance.
Individuals may decide not to intervene in critical situations if they are afraid of being superseded by a superior helper, offering unwanted assistance, or facing the legal consequences of offering inferior and possibly dangerous assistance.
3. Pluralistic Ignorance
The third process is pluralistic ignorance, which results from the tendency to rely on the overt reactions of others when defining an ambiguous situation.
Pluralistic ignorance occurs when a person does not agree with a certain type of thinking but believes that everyone else adheres to it and as a result, follows that line of thinking even though no one believes it.
An example of this is cited by Deborah A. Prentice. Despite being in a difficult class, students may not raise their hands in response to the lecturer asking for questions.
This is often due to the belief that everyone else understands the material; so for the fear of looking inadequate, no one asks clarifying questions.
It is this type of thinking that explains the effect of pluralistic ignorance on the bystander effect. The overarching idea is uncertainty and perception. What separates pluralistic ignorance is the ambiguousness that can define a situation.
If the situation is clear (for the classroom example: someone stating they do not understand), pluralistic ignorance would not apply (since the person knows that someone else agrees with their thinking).
It is the ambiguity and uncertainty which leads to incorrect perceptions that categorize pluralistic ignorance.
Rendsvig (2014) proposes an eleven step process to explain this phenomenon.
These steps follow the perspective of a bystander (who will be called Bystander A) amidst a group of other bystanders in an emergency situation.
- Bystander A is present in a specific place. Nothing has happened.
- A situation occurs that is ambiguous in nature (it is not certain what has occurred or what the ramifications of the event are) and Bystander A notices it.
- Bystander A believes that this is an emergency situation but is unaware of how the rest of the bystanders perceive the situation.
- A course of action is taken. This could be a few things like charging into the situation or calling the police, but in pluralistic ignorance, Bystander A chooses to understand more about the situation by looking around and taking in the reactions of others.
- As observation takes place, Bystander A is not aware that the other bystanders may be doing the same thing. Thus, when surveying others’ reactions, Bystander A “misperceives” the other bystanders' observation of the situation as purposeful inaction.
- As Bystander A notes the reaction of the others, Bystander A puts the reaction of the other bystanders in context.
- Bystander A then believes that the inaction of others is due to their belief that an emergency situation is not occurring.
- Thus, Bystander A believes that there is an accident but also believes that others do not perceive the situation as an emergency. Bystander A then changes their initial belief.
- Bystander A now believes that there is no emergency.
- Bystander A has another opportunity to help.
- Bystander A chooses not to help because of the belief that there is not an emergency.
Pluralistic ignorance operates under the assumption that all the other bystanders are also going through these eleven steps.
Thus, they all choose to not help due to the misperception of others' reactions to the same situation.
Other Explanations
While these three are the most widely known explanations, there are other theories that could also play a role. One example is confusion of responsibility.
Confusion of responsibility occurs when a bystander fears that helping could lead others’ to believing that they are the perpetrator. This fear can cause people to not act in dire situations.
Another example is priming. Priming occurs when a person is given cues that will influence future actions. For example, if a person is given a list of words that are associated with home decor and furniture, and then are asked to give a five-letter word, answers like chair or table would be more likely than pasta.
In social situations, Garcia et al. found that simply thinking of being in a group could lead to lower rates of helping in emergency situations. This occurs because groups are often associated with, “being lost in a crowd, being deindividuated, and having a lowered sense of personal accountability” (Garcia et al., 2002, p. 845).
Thus, the authors argue that the way a person was primed could also influence their ability to help. These alternate theories highlight the fact that the bystander effect is a complex phenomenon that encompasses a variety of ideologies.
Bystander Effect and Diffusion of Responsibility | Simply Psychology
https://www.simplypsychology.org/bystander-effect.html
We Are All Bystanders
But we don’t have to be. Dacher Keltner and Jason Marsh explain why we sometimes shackle our moral instincts, and how we can set them free.BY JASON MARSH, DACHER KELTNER | SEPTEMBER 1, 2006
For more than 40 years, Peggy Kirihara has felt guilty about Stewart.
Peggy liked Stewart. They went to high school together. Their fathers were friends, both farmers in California’s Central Valley, and Peggy would always say “hi” when she passed Stewart in the hall.
Yet every day when Stewart boarded their school bus, a couple of boys would tease him mercilessly. And every day, Peggy would just sit in her seat, silent.
“I was dying inside for him,” she said. “There were enough of us on the bus who were feeling awful—we could have done something. But none of us said anything.”
Peggy still can’t explain why she didn’t stick up for Stewart. She had known his tormenters since they were all little kids, and she didn’t find them threatening. She thinks if she had spoken up on his behalf, other kids might have chimed in to make the teasing stop.
 © Damian King
© Damian King
But perhaps most surprising—and distressing—to Peggy is that she considers herself an assertive and moral person, yet those convictions aren’t backed up by her conduct on the bus.
“I think I would say something now, but I don’t know for sure,” she said. “Maybe if I saw someone being beaten up and killed, I’d just stand there. That still worries me.”
Many of us share Peggy’s concern. We’ve all found ourselves in similar situations: the times we’ve seen someone harassed on the street and didn’t intervene; when we’ve driven past a car stranded by the side of the road, assuming another driver would pull over to help; even when we’ve noticed litter on the sidewalk and left it for someone else to pick up. We witness a problem, consider some kind of positive action, then respond by doing… nothing. Something holds us back. We remain bystanders.
Why don’t we help in these situations? Why do we sometimes put our moral instincts in shackles? These are questions that haunt all of us, and they apply well beyond the fleeting scenarios described above. Every day we serve as bystanders to the world around us—not just to people in need on the street but to larger social, political, and environmental problems that concern us, but which we feel powerless to address on our own. Indeed, the bystander phenomenon pervades the history of the past century.
“The bystander is a modern archetype, from the Holocaust to the genocide in Rwanda to the current environmental crisis,” says Charles Garfield, a clinical professor of psychology at the University of California, San Francisco, School of Medicine who is writing a book about the psychological differences between bystanders and people who display “moral courage.”
“Why,” asked Garfield, “do some people respond to these crises while others don’t?”
In the shadow of these crises, researchers have spent the past few decades trying to answer Garfield’s question. Their findings reveal a valuable story about human nature: Often, only subtle differences separate the bystanders from the morally courageous people of the world. Most of us, it seems, have the potential to fall into either category. It is the slight, seemingly insignificant details in a situation that can push us one way or the other.
Researchers have identified some of the invisible forces that restrain us from acting on our own moral instincts while also suggesting how we might fight back against these unseen inhibitors of altruism. Taken together, these results offer a scientific understanding for what spurs us to everyday altruism and lifetimes of activism, and what induces us to remain bystanders.
Altruistic inertia
Among the most infamous bystanders are 38 people in Queens, New York, who in 1964 witnessed the murder of one of their neighbors, a young woman named Kitty Genovese (see sidebar).
A serial killer attacked and stabbed Genovese late one night outside her apartment house, and these 38 neighbors later admitted to hearing her screams; at least three said they saw part of the attack take place. Yet no one intervened.
While the Genovese murder shocked the American public, it also moved several social psychologists to try to understand the behavior of people like Genovese’s neighbors.
One of those psychologists was John Darley, who was living in New York at the time. Ten days after the Genovese murder, Darley had lunch with another psychologist, Bibb Latané, and they discussed the incident.
“The newspaper explanations were focusing on the appalling personalities of those who saw the murder but didn’t intervene, saying they had been dehumanized by living in an urban environment,” said Darley, now a professor at Princeton University. “We wanted to see if we could explain the incident by drawing on the social psychological principles that we knew.”
A main goal of their research was to determine whether the presence of other people inhibits someone from intervening in an emergency, as had seemed to be the case in the Genovese murder. In one of their studies, college students sat in a cubicle and were instructed to talk with fellow students through an intercom. They were told that they would be speaking with one, two, or five other students, and only one person could use the intercom at a time.
There was actually only one other person in the study—a confederate (someone working with the researchers). Early in the study, the confederate mentioned that he sometimes suffered from seizures. The next time he spoke, he became increasingly loud and incoherent; he pretended to choke and gasp. Before falling silent, he stammered:
If someone could help me out it would it would er er s-s-sure be sure be good… because er there er er a cause I er I uh I’ve got a a one of the er sei-er-er things coming on and and and I could really er use some help… I’m gonna die er er I’m gonna die er help er er seizure er…
Eighty-five percent of the participants who were in the two-person situation, and hence believed they were the only witness to the victim’s seizure, left their cubicles to help. In contrast, only 62 percent of the participants who were in the three-person situation and 31 percent of the participants in the six-person situation tried to help.
Darley and Latané attributed their results to a “diffusion of responsibility”: When study participants thought there were other witnesses to the emergency, they felt less personal responsibility to intervene. Similarly, the witnesses of the Kitty Genovese murder may have seen other apartment lights go on, or seen each other in the windows, and assumed someone else would help. The end result is altruistic inertia. Other researchers have also suggested the effects of a “confusion of responsibility,” where bystanders fail to help someone in distress because they don’t want to be mistaken for the cause of that distress.
Darley and Latané also suspected that bystanders don’t intervene in an emergency because they’re misled by the reactions of the people around them. To test this hypothesis, they ran an experiment in which they asked participants to fill out questionnaires in a laboratory room. After the participants had gotten to work, smoke filtered into the room—a clear signal of danger.
When participants were alone, 75 percent of them left the room and reported the smoke to the experimenter. With three participants in the room, only 38 percent left to report the smoke. And quite remarkably, when a participant was joined by two confederates instructed not to show any concern, only 10 percent of the participants reported the smoke to the experimenter.
The passive bystanders in this study succumbed to what’s known as “pluralistic ignorance”—the tendency to mistake one another’s calm demeanor as a sign that no emergency is actually taking place. There are strong social norms that reinforce pluralistic ignorance. It is somewhat embarrassing, after all, to be the one who loses his cool when no danger actually exists. Such an effect was likely acting on the people who witnessed the Kitty Genovese incident; indeed, many said they didn’t realize what was going on beneath their windows and assumed it was a lover’s quarrel. That interpretation was reinforced by the fact that no one else was responding, either.
A few years later, Darley ran a study with psychologist Daniel Batson that had seminary students at Princeton walk across campus to give a talk. Along the way, the students passed a study confederate, slumped over and groaning in a passageway. Their response depended largely on a single variable: whether or not they were late. Only 10 percent of the students stopped to help when they were in a hurry; more than six times as many helped when they had plenty of time before their talk.
Lateness, the presence of other people—these are some of the factors that can turn us all into bystanders in an emergency. Yet another important factor is the characteristics of the victim. Research has shown that people are more likely to help those they perceive to be similar to them, including others from their own racial or ethnic groups. In general, women tend to receive more help than men. But this varies according to appearance: More attractive and femininely dressed women tend to receive more help from passersby, perhaps because they fit the gender stereotype of the vulnerable female.
We don’t like to discover that our propensity for altruism can depend on prejudice or the details of a particular situation—details that seem beyond our control. But these scientific findings force us to consider how we’d perform under pressure; they reveal that Kitty Genovese’s neighbors might have been just like us. Even more frightening, it becomes easier to understand how good people in Rwanda or Nazi Germany remained silent against the horrors around them. Afraid, confused, coerced, or willfully unaware, they could convince themselves that it wasn’t their responsibility to intervene.
But still, some did assume this responsibility, and this is the other half of the bystander story. Some researchers refer to the “active bystander,” that person who witnesses an emergency, recognizes it as such, and takes it upon herself to do something about it.
Who are these people? Are they inspired to action because they receive strong cues within a situation, indicating it’s an emergency? Or is there a particular set of characteristics—a personality type—that makes some people more likely to be active bystanders while others remain passive?
Why people help
A leader in the study of the differences between active and passive bystanders is psychologist Ervin Staub, whose research interests were shaped by his experiences as a young Jewish child in Hungary during World War II.
“I was to be killed in the Holocaust,” he said. “And there were important bystanders in my life who showed me that people don’t have to be passive in the face of evil.” One of these people was his family’s maid, Maria, a Christian woman who risked her life to shelter Staub and his sister while 75 percent of Hungary’s 600,000 Jews were killed by the Nazis.
Staub has tried to understand what motivates the Marias of the world. Some of his research has put a spin on the experimental studies pioneered by Darley and Latané, exploring what makes people more likely to intervene rather than serve as passive bystanders.
In one experiment, a study participant and a confederate were placed in a room together, instructed to work on a joint task. Soon afterwards, they heard a crash and cries of distress. When the confederate dismissed the sounds—saying something like, “That sounds like a tape. .. Or I guess it could be part of another experiment.”—only 25 percent of the participants went into the next room to try to help. But when the confederate said, “That sounds bad. Maybe we should do something,” 66 percent of the participants took action. And when the confederate added that participants should go into the next room to check out the sounds, every single one of them tried to help.
In another study, Staub found that kindergarten and first grade children were actually more likely to respond to sounds of distress from an adjoining room when they were placed in pairs rather than alone. That seemed to be the case because, unlike the adults in Darley and Latané’s studies, the young children talked openly about their fears and concerns, and together tried to help.
These findings suggest the positive influence we can exert as bystanders. Just as passive bystanders reinforce a sense that nothing is wrong in a situation, the active bystander can, in fact, get people to focus on a problem and motivate them to take action.
John Darley has also identified actions a victim can take to get others to help him. One is to make his need clear—“I’ve twisted my ankle and I can’t walk; I need help”—and the other is to select a specific person for help—“You there, can you help me?” By doing this, the victim overcomes the two biggest obstacles to intervention. He prevents people from concluding there is no real emergency (thereby eliminating the effect of pluralistic ignorance), and prevents them from thinking that someone else will help (thereby overcoming diffusion of responsibility).
But Staub has tried to take this research one step further. He has developed a questionnaire meant to identify people with a predisposition toward becoming active bystanders. People who score well on this survey express a heightened concern for the welfare of others, greater feelings of social responsibility, and a commitment to moral values—and they also prove more likely to help others when an opportunity arises.
Similar research has been conducted by sociologist Samuel Oliner. Like Staub, Oliner is a Holocaust survivor whose work has been inspired by the people who helped him escape the Nazis. With his wife Pearl, a professor of education, he conducted an extensive study into “the altruistic personality,” interviewing more than 400 people who rescued Jews during the Holocaust, as well as more than 100 nonrescuers and Holocaust survivors alike. In their book The Altruistic Personality, the Oliners explain that rescuers shared some deep personality traits, which they described as their “capacity for extensive relationships—their stronger sense of attachment to others and their feelings of responsibility for the welfare of others.” They also found that these tendencies had been instilled in many rescuers from the time they were young children, often stemming from parents who displayed more tolerance, care, and empathy toward their children and toward people different from themselves.
“I would claim there is a predisposition in some people to help whenever the opportunity arises,” said Oliner, who contrasts this group to bystanders. “A bystander is less concerned with the outside world, beyond his own immediate community. A bystander might be less tolerant of differences, thinking ‘Why should I get involved? These are not my people. Maybe they deserve it?’ They don’t see helping as a choice. But rescuers see tragedy and feel no choice but to get involved. How could they stand by and let another person perish?”
Kristen Monroe, a political scientist at the University of California, Irvine, has reached a similar conclusion from her own set of interviews with various kinds of altruists. In her book The Heart of Altruism, she writes of the “altruistic perspective,” a common perception among altruists “that they are strongly linked to others through a shared humanity.”
But Monroe cautions that differences are often not so clear cut between bystanders, perpetrators, and altruists.
“We know that perpetrators can be rescuers and some rescuers I’ve interviewed have killed people,” she said. “It’s hard to see someone as one or the other because they cross categories. Academics like to think in categories. But the truth is that it’s not so easy.”
Indeed, much of the bystander research suggests that one’s personality only determines so much. To offer the right kind of help, one also needs the relevant skills or knowledge demanded by a particular situation.
As an example, John Darley referred to his study in which smoke was pumped into a room to see whether people would react to that sign of danger. One of the participants in this study had been in the Navy, where his ship had once caught on fire. So when this man saw the smoke, said Darley, “He got the hell out and did something, because of his past experiences.” There’s an encouraging implication of these findings: If given the proper tools and primed to respond positively in a crisis, most of us have the ability to transcend our identities as bystanders.
“I think that altruism, caring, social responsibility is not only doable, it’s teachable,” said Oliner.
And in recent years, there have been many efforts to translate research like Oliner’s into programs that encourage more people to avoid the traps of becoming a bystander.
Anti-bystander education
Ervin Staub has been at the fore of this anti-bystander education. In the 1990s, in the wake of the Rodney King beating, he worked with California’s Department of Justice to develop a training program for police officers. The goal of the program was to teach officers how they could intervene when they feared a fellow officer was about to use too much force.
“The police have a conception, as part of their culture, that the way you police a fellow officer is to support whatever they’re doing, and that can lead to tragedy, both for the citizens and the police themselves,” said Staub. “So here the notion was to make police officers positive active bystanders, getting them engaged early enough so that they didn’t have to confront their fellow officer.”
More recently, Staub helped schools in Massachusetts develop an anti-bystander curriculum, intended to encourage children to intervene against bullying. The program draws on earlier research that identified the causes of bystander behavior. For instance, older students are reluctant to discuss their fears about bullying, so each student tacitly accepts it, afraid to make waves, and no one identifies the problem—a form of pluralistic ignorance. Staub wants to change the culture of the classroom by giving these students opportunities to air their fears.
“If you can get people to express their concern, then already a whole different situation exists,” he said.
This echoes a point that John Darley makes: More people need to learn about the subtle pressures that can cause bystander behavior, such as diffusion of responsibility and pluralistic ignorance. That way they’ll be better prepared next time they encounter a crisis situation. “We want to explode one particular view that people have: ‘Were I in that situation, I would behave in an altruistic, wonderful way,’” he said. “What I say is, ‘No, you’re misreading what’s happening. I want to teach you about the pressures [that can cause bystander behavior]. Then when you feel those pressures, I want that to be a cue that you might be getting things wrong.’”
Research suggests that this kind of education is possible. One set of studies even found that people who attended social psychology lectures about the causes of bystander behavior were less susceptible to those influences.
But of course, not even this form of education is a guarantee against becoming a bystander. We’re always subject to the complicated interaction between our personal disposition and the demands of circumstance. And we may never know how we’ll act until we find ourselves in a crisis.
To illustrate this point, Samuel Oliner told the story of a Polish brickmaker who was interviewed for Oliner’s book, The Altruistic Personality. During World War II, a Jewish man who had escaped from a concentration camp came to the brickmaker and pleaded for help. The brickmaker turned him away, saying he didn’t want to put his own family at risk. “So is he evil?” asked Oliner. “I wouldn’t say he’s evil. He couldn’t act quickly enough, I suppose, to say, ‘Hide in my kiln,’ or ‘Hide in my barn.’ He didn’t think that way.”
“If I was the bricklayer and you came to me, and the Nazis were behind you and the Gestapo was chasing you—would I be willing to help? Would I be willing to risk my family? I don’t know. I don’t know if I would be.”
https://greatergood.berkeley.edu/article/item/we_are_all_bystanders
Bystander effect
The bystander effect, or bystander apathy, is a social psychological theory that states that individuals are less likely to offer help to a victim when there are other people present. First proposed in 1964, much research, mostly in the lab, has focused on increasingly varied factors, such as the number of bystanders, ambiguity, group cohesiveness, and diffusion of responsibility that reinforces mutual denial. The theory was prompted by the murder of Kitty Genovese about which it was wrongly reported that 38 bystanders watched passively. Recent research has focused on "real world" events captured on security cameras, and the coherency and robustness of the effect has come under question.[1] More recent studies also show that this effect can generalize to workplace settings, where subordinates often refrain from informing managers regarding ideas, concerns, and opinions.[2]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bystander_effect